Breakthrough study reveals biological basis for sensory processing disorders in kids
Sensory processing disorders (SPD) are more prevalent in children than autism and as common as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, yet the condition receives far less attention partly because it's never been recognized as a distinct disease.
In a groundbreaking new study from UC San Francisco, researchers have found that children affected with SPD have quantifiable differences in brain structure, for the first time showing a biological basis for the disease that sets it apart from other neurodevelopmental disorders.
One of the reasons SPD has been overlooked until now is that it often occurs in children who also have ADHD or autism, and the disorders have not been listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual used by psychiatrists and psychologists.
'OUT OF SYNC' KIDS
Sensory processing disorders affect 5 to 16 percent of school-aged children.
Children with SPD struggle with how to process stimulation, which can cause a wide range of symptoms including hypersensitivity to sound, sight and touch, poor fine motor skills and easy distractibility. Some SPD children cannot tolerate the sound of a vacuum, while others can't hold a pencil or struggle with social interaction. Furthermore, a sound that one day is an irritant can the next day be sought out. The disease can be baffling for parents and has been a source of much controversy for clinicians, according to the researchers.
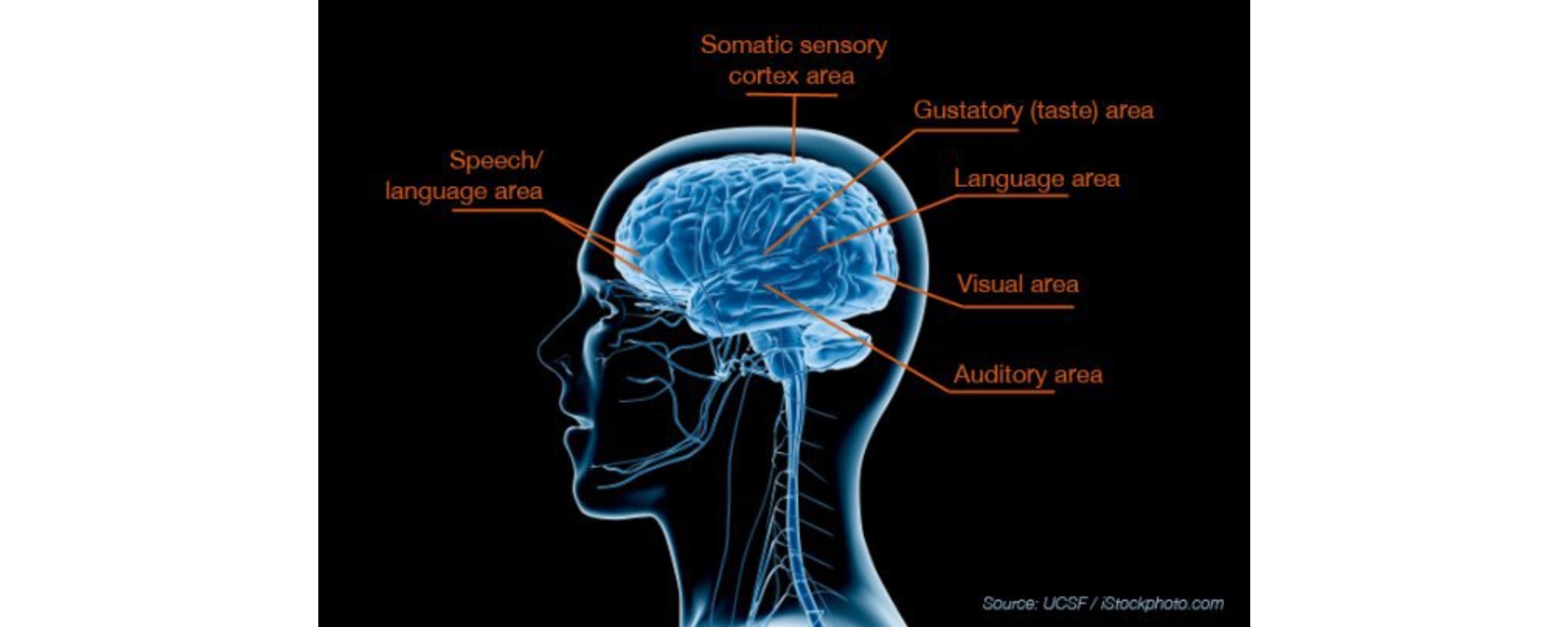
IMAGING THE BRAIN'S WHITE MATTER
In the study, researchers used an advanced form of MRI called diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), which measures the microscopic movement of water molecules within the brain in order to give information about the brain's white matter tracts. DTI shows the direction of the white matter fibers and the integrity of the white matter. The brain's white matter is essential for perceiving, thinking and learning.

Πηγή: The Sensory Spectrum
